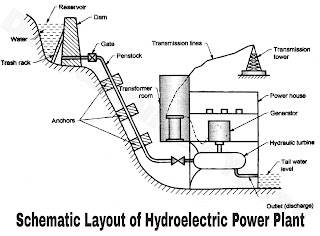
Schematic Layout of Hydro Electric Power Plant
Q. What is layout of hydroelectric power plant?
Q. How is hydro power plant constructed?
Q. What are the different parts of a hydroelectric power plant?
A schematic layout of hydro-electric power plant is shown in Figure A large amount of water is collected during rainy season in a reservoir behind a dam. In case the rainfall is low in a particular year the low head of the reservoir will not be able to meet the maximum load, therefore, the present trend is to use hydro-electric power plant with steam power plant an interconnected system.
The main components of the hydro-electric power plant and their functions are a follows :
1. Reservoir : A reservoir is provided to store water during rainy season and supplies the same in dry season. The water from the reservoir is used to run the hydraulic turbine.2. Dam : A dam is structure of considerable height built across the river. Its function is to provide working head of water for power plant and to increase the storage capacity of reservoir.
3. Trash rack : These are made up of steel bars. Trash rack is provided to prevent entry of debris into the intakes from dam or from the forebays. Any debris into the intake water pipe may damage the turbine runners or choke the nozzles of an impulse turbine.
4. Gate : The gate is provided for controlling of flow of water from reservoir to hydraulic turbine through penstock . It is closed when maintenance of system is required.
5. Forebays : It is small water reservoir at the end of water passage from the reservoir and before the water is fed to the turbine to the penstock as shown in Figure B.
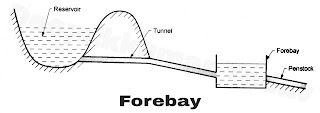 |
| Figure B |
It acts as a temporary regulating reservoir. It stores water when the load on the plant reduces and the same water is supplied to the turbine at the time of increasing load in the initial stages. It helps in absorbing the flow variations.
6. Surge tank :
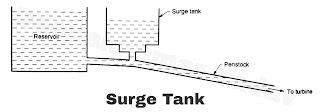 |
| Figure C |
In case the load on the turbine suddenly decreases, the gates admitting water to the turbine are suddenly closed due to governor action. As a result it reduces the water flow with sudden increase of pressures in the penstock. This sudden rise of pressure in penstock is called "Water Hammer".
On the other hand, due to sudden increased load on the turbine, the gates admitting water to the turbine are suddenly opened. It causes water to rush from penstock into the turbine and it creates a vacuum in the penstock.
Therefore, penstock is subjected to positive pressure (water hammer) due to sudden decrease in load on the turbine and to negative pressure due to sudden increase in load on the turbine.
In order to provide better regulation of water pressure in the system, a surge tank is used which is located near the power house on high ground. When the turbine gates are closed and water flow to the turbine reduces, the water rises into the surge tank. It produces a retarding head with reduced velocity of water in the penstock. As soon as the velocity of water in the penstock is reduced to a value corresponding to the level of the turbine, the level of water in the surge tank starts falling and fluctuates up and down until its motion is damped out by friction.
Similarly, during the increase load on the turbine, additional water flows from the surge tank to the turbine. It produces an accelerating head which increases the velocity of flow of water in the penstock
Therefore, a surge tank helps in establishing the velocity and pressure in the penstock and it reduces the water hammer effect.
7. Waterway and penstock : A waterway is used to carry water from the dam to the power house. It includes canal and penstock (closed pipe) or a tunnel. The penstock are made up of steel of reinforced concrete which are designed to withstand high pressures. Penstock are supported by anchors. Sharp bends in penstocks are avoided in order to reduce the hydraulic losses.
8. Spillway : A spillway is provided to discharge the flood water and to keep the level of water below the designed maximum level in the reservoir . Thus a spillway saves the dam from damage during floods.
9. Power house : A power house consists of hydraulic and electric equipments where the water energy is converted into electrical energy. Usually the power house is located underground whenever possible e.g. as in case of Koyana power house in Maharashtra state.
10. Hydraulic turbines : These are used to convert the kinetic energy of water into mechanical energy.
11. Draft tube : A draft tube is a passage which connects the exit from the turbine runner down to tail race water level. It supplements the action of runner of the reaction turbine by utilising the remainder K.E. of the water at discharge end of the runner. Another purpose of the draft tube is to permit the setting of the runner of the reaction turbine wheel at a level above that of water in the tail race under high water and flood conditions of the river.
12. Tail race : A tail race is a water way to lead the water discharged from the turbine to the river.
Operation of hydro-electric power plant :
Water from reservoir flows through penstocks to hydraulic turbine and during the passage its potential energy (water head) is converted into kinetic energy. This high velocity jet of water strikes the hydraulic turbine vanes where its K.E. is converted into mechanical energy.
A generator coupled to hydraulic turbine converts the available mechanical energy into electrical energy. The speed of the turbine and generator depends on the head, specific speed and the power.
The electrical power generated is controlled by the governing mechanism attached to hydraulic turbine which controls the quantity of water to be supplied to the turbine according to the load on the system.